Novel In-Air Gestures (Prototypes & User Research)
In-Air Gestures

About
This project involved a series of iterative interfaces that explore people’s ideal use of multi-modal inputs to control objects in their home environment. The process and results were published in the proceedings of OzChi 2013.
Videos
Mid-way through the project, we (Karen and I) presented the state of the project along with a few videos. The presentation can be found here [PDF].
Concept Video
A concept video was made by Karen for the presentation demonstrating the gestures in context.
A quick proof of technical concept video was also produced here.
Technical Video
This is the technical setup of the second prototype in the series of three iterations for this paper exploring multi-modal human-object interactions in the home environment.
This prototype consists of an LED lamp, Kinect, arduino, iPad, and laptop depicting the depth histogram of the user. The same setup depicted is used for participants in their selected environment, but the arduino, cables, and laptop are hidden.
Paper: Abstract
The home is an environment filled with an increasing number of fixtures and appliances, from doors and windows to kettles and chargers. Devices for in-air gestural recognition are also increasing in commercial availability. Appropriate attributes that make up natural in-air gestures have yet to be uniformly established, especially in relation to their use in the comfort of the home environment. Three studies were conducted, each informing the focus and construction of a gesture- recognition prototype for the following study. The preferred attributes of in-air gestures were examined; their use in conjunction with other modalities, the motion of in-air gestures, and feedback delay and transition time of an action as instigated by an in-air gesture. Our findings indicate natural actions that precede in-air gestures, topographical correlations between gesture and system response, and a desire for minimal effort. These results can be used as guidelines for the design of in-air gestures and systems for their recognition in environments within and beyond the home.
Links
- Original Student [PDF]
- Later published in the OzChi 2013 Proceedings: Favoured Attributes of In-Air Gestures in the Home Environment
Results: Graphs
User Satisfaction was measured against different interaction paradigms.
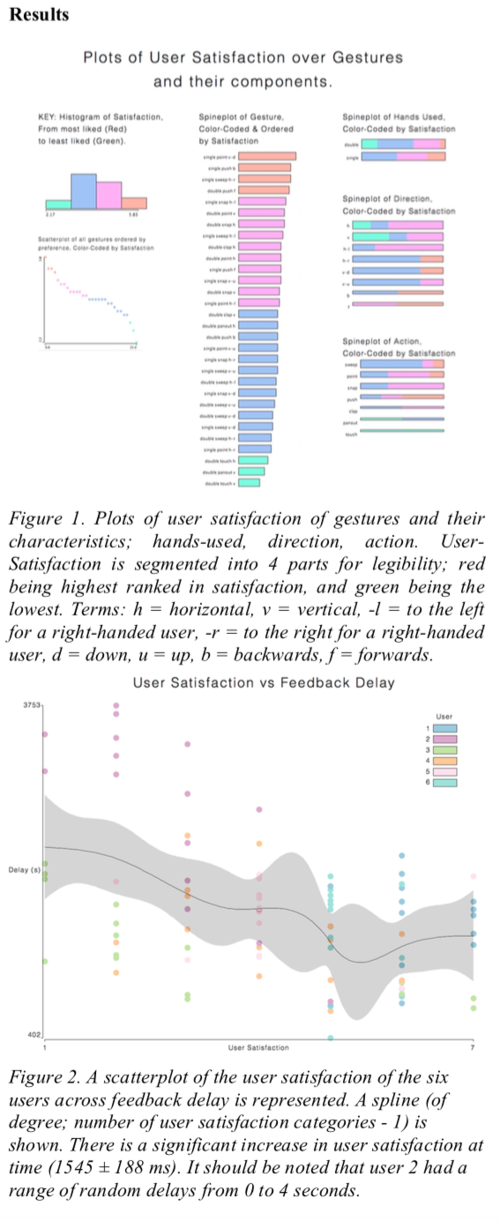
For a more indepth analysis of the results see the paper.
Team
Hanley Weng, Karen Ho.
Original paper advised by Dr Anne Marie Piper, OzChi revision advised by Dr Martin Tomitsch. Many thanks.
Tools
Mondrian, Kinect, Java, Processing, AttrakDiff, Mondrian